We’re excited to share our latest open-access publication in Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics:
“An interpretable machine learning framework with data-informed imaging biomarkers for diagnosis and prediction of Alzheimer’s disease”.
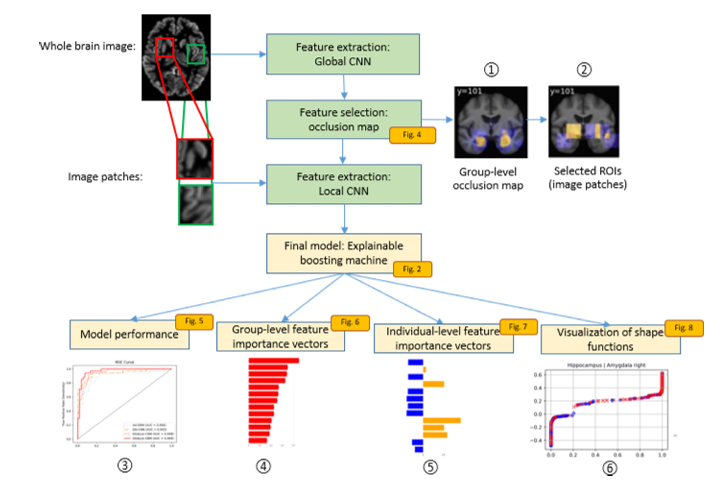
In this work, they (first author Wenjie Kang with co-authors, in particular, Bo, Esther, and Stefan from the BIGR) present Glo&Loc-EBM, an interpretable machine learning framework that integrates deep learning–derived imaging biomarkers with an inherently interpretable modeling approach for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) diagnosis and progression prediction.
The proposed framework combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for feature extraction from structural MRI with Explainable Boosting Machines (EBMs) to enable both high predictive performance and transparent decision-making. By incorporating global brain information and region-specific imaging biomarkers, the method provides interpretable insights at both group and individual levels while maintaining competitive accuracy compared with state-of-the-art black-box models.
The approach was validated on the ADNI cohort with external evaluation on an independent multi-center dataset, demonstrating strong performance for AD classification and prediction of mild cognitive impairment conversion, highlighting its potential for clinically trustworthy AI in neurodegenerative disease research.
This article is open access under CC BY in Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics (2026; Article 102722).
DOI: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2026.102722.