Sijie Liu and Ruisheng introduced a segmentation-assisted framework designed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of brain vessel centerline extraction from CTA images. Their considerable contribution were outlined in the paper, “Segmentation-assisted vessel centerline extraction from cerebral CT Angiography”.
In this work, they (Sijie Liu and Ruisheng who contributed equally with the co-authors, in particular, Aad van der Lugt who is the head of the Department Radiology & Nuclear Medicine and Wiro and Theo from the BIGR) present their work on segmentation-assisted vessel centerline extraction from cerebral CT Angiography (CTA).
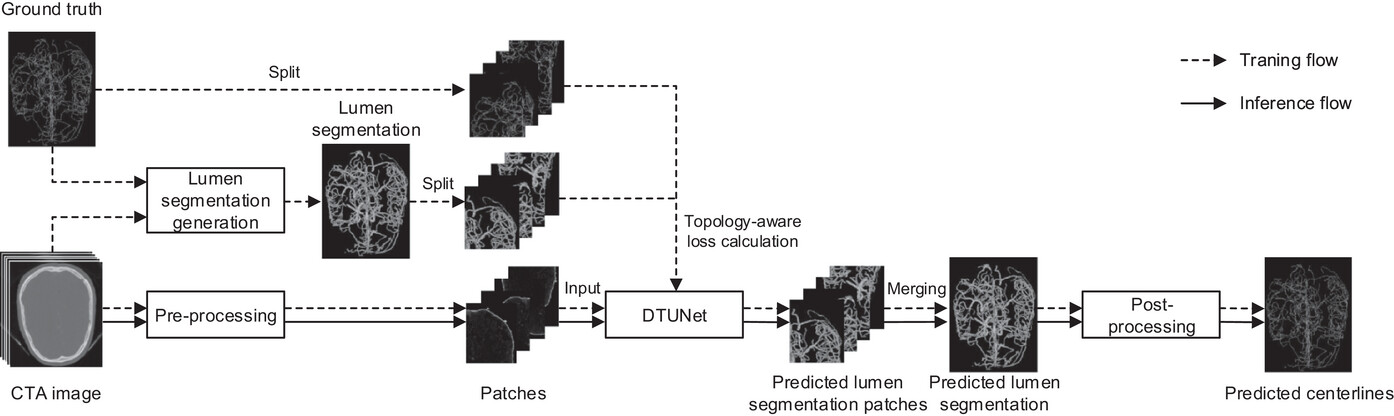
This study aimed to develop and validate a segmentation-assisted framework designed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of brain vessel centerline extraction from CTA images. As shown in the figure above, the framework integrates four modules: (1) pre-processing techniques that register CTA images with a CT atlas and divide these images into input patches, (2) lumen segmentation generation from annotated vessel centerlines using graph cuts and robust kernel regression, (3) a dual-branch topology-aware UNet (DTUNet) that optimizes the use of the annotated vessel centerlines and the generated lumen segmentation via a topology-aware loss (TAL) and its dual-branch structure, and (4) post-processing methods that skeletonize and refine the lumen segmentation predicted by the DTUNet.
They validated the proposed framework using an in-house dataset derived from a subset of the MR CLEAN Registry and found that DTUnet achieves high performance without introducing additional annotation demands by automating the process of lumen segmentation generation and optimizing the network design of vessel centerline extraction. They expected that this solution could be beneficial in various clinical applications in cerebrovascular disease management.
Read the full article here.