AFRICAI-RI is a new four-year European Union–funded research infrastructure project aiming to strengthen biomedical imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities across ten clinical research sites in Africa.
Respiratory diseases such as tuberculosis (TB) and pneumonia remain a major public health challenge in many parts of Africa. At the same time, access to large-scale, high-quality biomedical imaging data and advanced AI infrastructure is limited. AFRICAI-RI (Research Infrastructure for Biomedical Imaging and Artificial Intelligence in Respiratory Care) addresses this critical gap by establishing the first federated, multi-institution imaging data infrastructure on the African continent.
The project brings together international expertise to adapt successful European imaging and AI infrastructures—such as those developed in EuCanImage and EUCAIM—to the specific clinical, technical, and regulatory needs of African research environments. By doing so, AFRICAI-RI aims to enable secure data sharing, collaborative research, and privacy-preserving AI development across borders.
Federated and FAIR Imaging Infrastructure
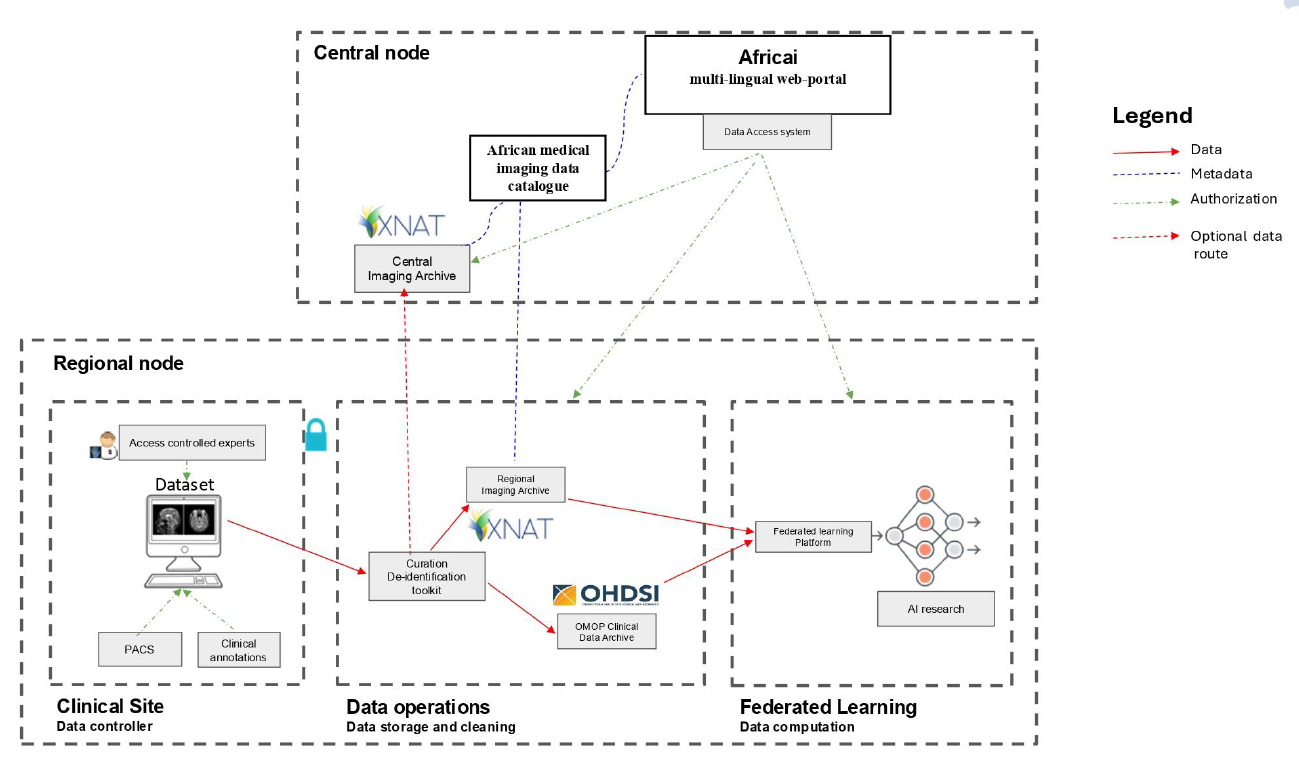
A central goal of AFRICAI-RI is to implement a federated and FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) research infrastructure. Imaging and clinical data will remain stored locally at each participating clinical site while being harmonized and anonymized to enable large-scale analysis.
The open-source imaging platform XNAT will be installed at all local sites to serve as the imaging archive. In addition, a central node will host a central XNAT archive and a data catalogue, enabling secure discovery of available datasets. Clinical data will be collected through a dedicated electronic case report form (eCRF) framework that complies with the OMOP data standard and is directly linked to the imaging data.
AI for Tuberculosis and Pneumonia Diagnosis
The primary use cases of AFRICAI-RI focus on applying AI to improve the diagnosis of tuberculosis and pneumonia in both adults and children. The project will leverage X-ray and chest ultrasound imaging, combined with clinical data, to develop and validate AI algorithms using federated learning techniques. This approach allows models to be trained across multiple sites without transferring sensitive patient data, thereby preserving privacy and data sovereignty.
BIGR Involvement
The Biomedical Imaging Group Rotterdam (BIGR) at Erasmus MC plays a central role in AFRICAI-RI. Researchers from BIGR contribute their expertise in medical image analysis, data management, and federated AI infrastructure.
The following BIGR members are directly involved in the AFRICAI-RI project:
Within the project, BIGR is responsible for leading key technical and infrastructural components, including the design and implementation of a federated and FAIR imaging research infrastructure. In addition, BIGR co-leads the infrastructure working group together with the Medical Research Council of The Gambia (MRCG), ensuring alignment between technical development and real-world clinical research needs.
Through AFRICAI-RI, BIGR contributes to building sustainable research infrastructure that enables collaborative AI development while respecting data privacy and local data ownership, ultimately supporting improved diagnosis and care for respiratory diseases in Africa.